Latest news
A review article titled "Model bacteria for biofouling research of reverse osmosis membranes" has been published in the journal Water Cycle (IF=8.3). The study was completed by the research group of Professor Hong Yu from Beijing Forestry University's College of Environmental Science & Engineering in collaboration with Professor Hu Hongying's team from Tsinghua University. The first author is PhD candidate Gao Yujia, with Professor Hong Yu and Associate Researcher Wu Yinhu from Tsinghua University serving as the corresponding authors. Beijing Forestry University is the signature unit of the first author.
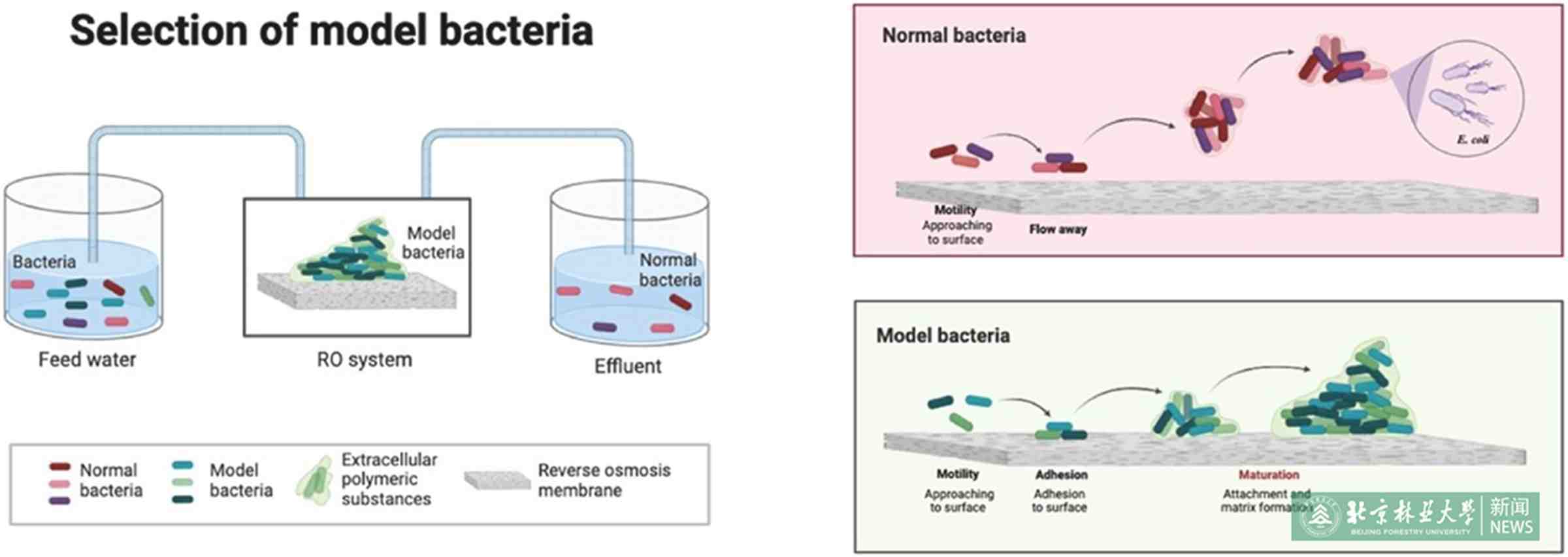
The selection of suitable model bacteria is closely related to biofouling control and mechanism verification. In this work, we discussed the necessity of model bacteria for biofouling research and control. According to our investigation, bacteria can only be defined as model bacteria if three conditions are met: 1) robust attachment capacity to the RO membrane surface; 2) high relative abundance; and 3) high biofouling potential. More importantly, a list of reverse osmosis (RO) biofouling-related model bacteria was given for subsequent research. Bacteria with high secretion capacity tend to cause more severe biofouling. Notably, potential disinfection-resistant bacteria (DRB), which possessed high capacity in extracellular polymeric substance secretion and biofilm formation, were prevalent in fouled RO membranes and deserved priority attention. With the proposed criteria, we hope to provide new insights and principles for selecting model bacteria in RO membrane technology development.
This work was financially supported by the Science Fund for Creative Research Groups (No. 52221004), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52470041), and the Major Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52293440 No. 52293442. )
Paper Link: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watcyc.2025.03.005
Written by Gao Yujia
Translated and edited by Song He
Reviewed by Yu Yangyang












