Latest news
Professor Peng Feng's team at Beijing Forestry University's College of Material Science and Technology has engineered a reusable hot-melt adhesive from industrial byproduct xylan. Published in Nature Sustainability (IF=25.7), this innovation transforms pulp waste into high-strength glue, outperforming petroleum-based rivals while solving plastic pollution challenges.

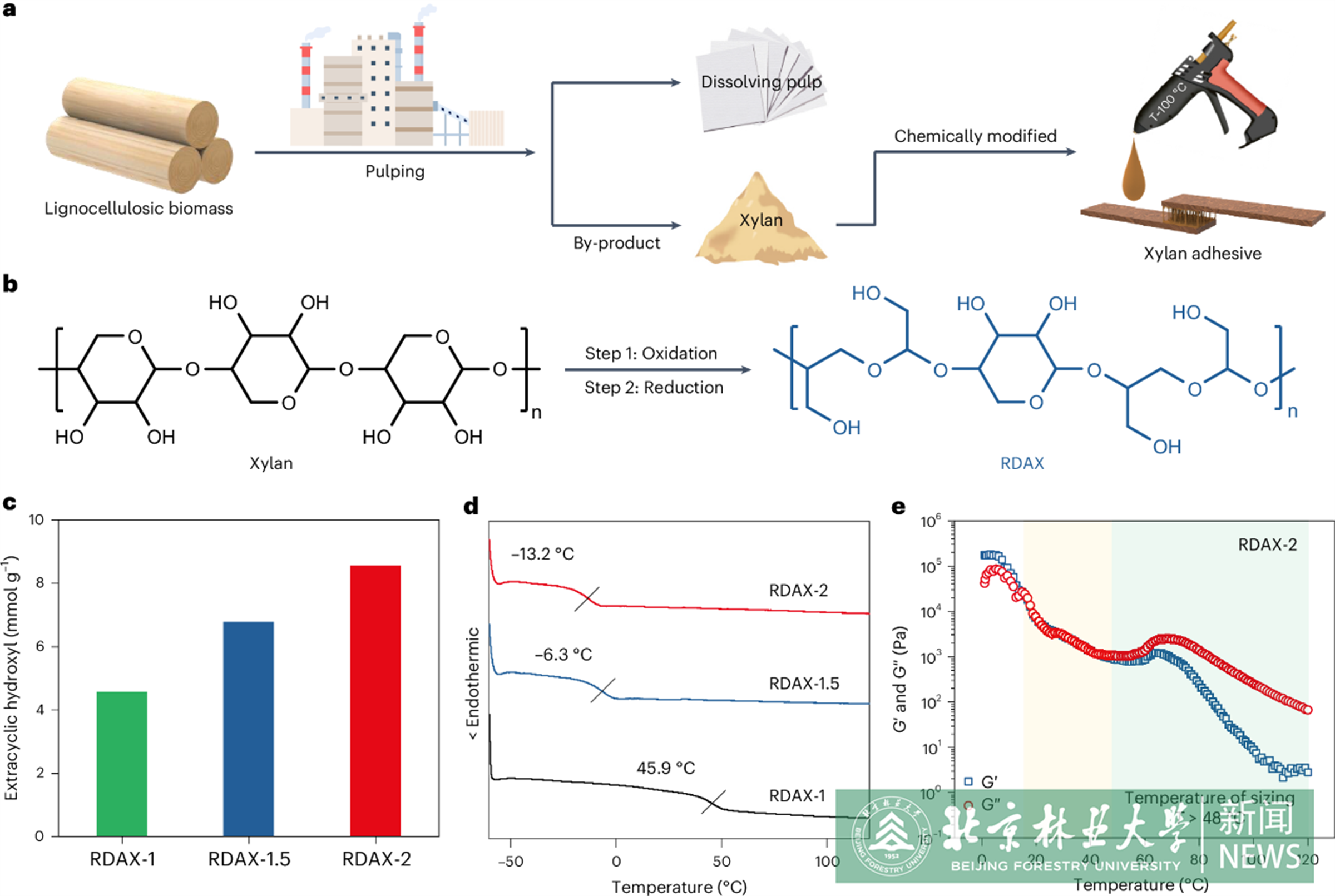
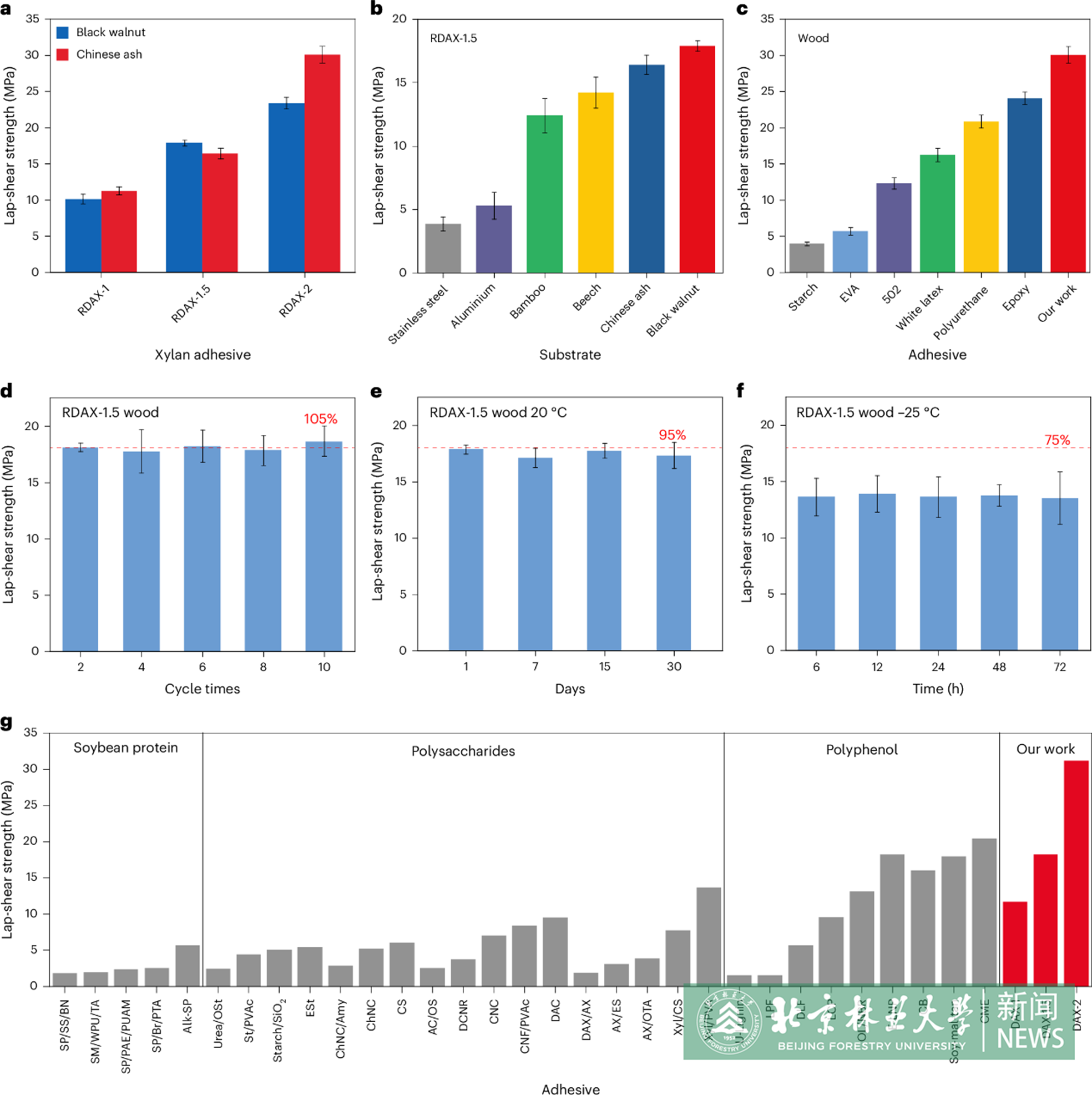
Adhesives are ubiquitous in industries and daily life. However, conventional fossil-derived adhesives pose substantial health and environmental risks during manufacturing and utilization. The development of nontoxic high-performance adhesives from renewable feedstocks is therefore highly desired but remains technically challenging. Here we report a high-performing hot-melt adhesive—glue that is applied in a hot molten state—derived from a byproduct of the pulp industry, xylan, a type of hemicellulose. Under optimal conditions, the lap-shear strength between wood chips can reach approximately 30 MPa, surpassing that of classic epoxy resins and far exceeding that of a commercial hot-melt adhesive (ethylene vinyl acetate). Furthermore, the xylan hot-melt adhesive exhibits excellent reusability for multiple applications, retaining more than 100% of its original adhesion strength even after ten reuse cycles. Toxicity tests show good biocompatibility for xylan hot-melt adhesive. Overall, this work provides useful insights into the design of high-performance, reusable, bio-based adhesives for enhanced sustainability.
Lü Ziwen, a Ph.D candidate at the School of Materials Science and Technology, is the first author of the paper. Youth teacher Rao Jun and Professor Peng Feng are the co-corresponding authors. Beijing Forestry University is the signature unit of the first author.
The study was supported by National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars (32225034), 111 Project (BP0820033), and National Natural Science Foundation of China (22278036).
Paper link: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41893-025-01579-9
Written by Lü Ziwen
Translated and edited by Song He
Reviewed by Yu Yangyang










