Latest news
Recently, Professor Yan Dang's research team from the College of Environmental Science & Engineering published a paper entitled "Evidence of autotrophic direct electron transfer denitrification (DETD) by Thiobacillus species enriched on biocathodes during deep polishing of effluent from a municipal wastewater treatment plant" in the Q1 journal Chemical Engineering Journal (IF=13.3). The research focuses on deep denitrification based on direct electron transfer.
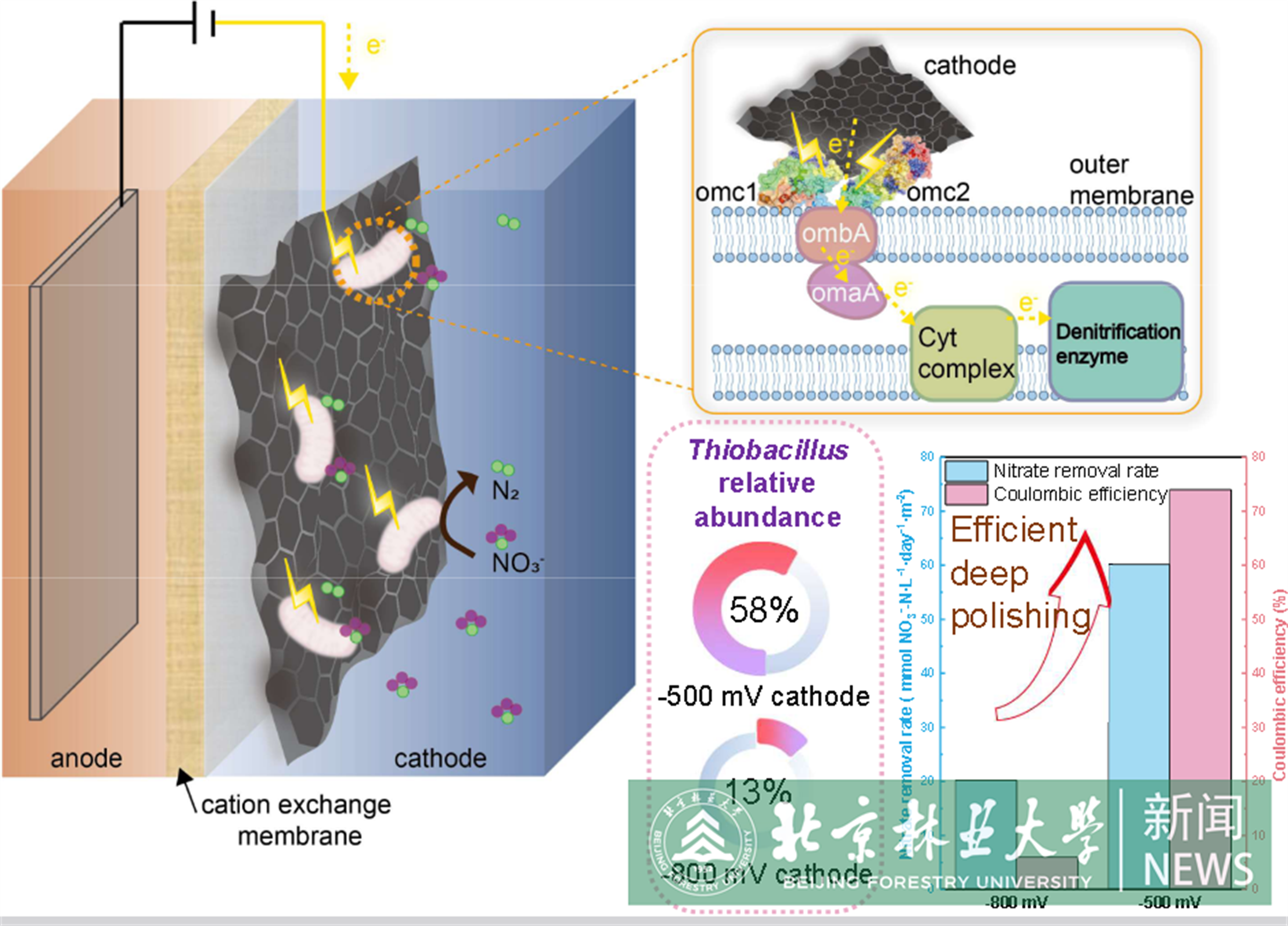
Cathodes can play a pivotal role as electron donors for denitrification in wastewater treatment plants, facilitating the removal of nitrogen-containing compounds such as nitrate. Denitrifying bacteria can either accept electrons directly from the electrode or indirectly via electron shuttling intermediaries generated at the cathode. In this study, comparative analyses were conducted between two denitrifying electrochemical reactors with biocathodes poised at different potentials, one that generated H2 through water electrolysis and one that did not (−500 mV and −800 mV vs. SHE). Nitrogen removal efficiencies were much higher in the −500 mV (vs. SHE) system, >93 % compared to only 20 %. Notably, a biofilm formed exclusively on the −500 mV (vs. SHE) cathode, predominantly composed of Thiobacillus species, with the majority most similar to Thiobacillus strain 65-29. Metatranscriptomics showed that genes from Thiobacillus strain 65-29 encoding outer surface c-type cytochrome and porin proteins that could facilitate direct electron uptake, were markedly up-regulated in the −500 mV (vs. SHE) reactor. Reduced sulfur species generated by the cathode and sulfate reducing bacteria might have also provided a source of electrons for nitrate reduction. In fact, Thiobacillus in the −500 mV (vs. SHE) system exhibited elevated expression of genes involved in thiosulfate (soxABXYZ), sulfite (soeABC), and sulfide (fccAB) oxidation. These findings offer valuable insights into the mechanisms of autotrophic denitrification by Thiobacillus in mixed culture systems and provide practical guidance for engineering applications.
The first author of the paper is Li Haoyong, a doctoral student from the College of Environmental Science & Engineering, with Professors Yan Dang and Bin Qiu serving as corresponding authors. Beijing Forestry University is the signature unit of the first author.
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52270023), the China Baowu Low Carbon Metallurgy Innovation Foundation (No. BWLCF202214), and the Engineering Research & Innovation Team Project of Beijing Forestry University (No. BLRC2023B04).
Paper link: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2024.153389
Written by Li Haoyong
Translated and edited by Song He
Reviewed by Yu Yangyang












