Latest news
Literature review "Resource utilization of carbon dioxide and nitrate to produce value-added organonitrogen compounds through an electrochemical approach" by Professor Wang Hui's research group from the College of Environmental Science and Engineering was published in "Applied Catalysis B"(IF=22.1), a Top journal in environment. The first author is Yu Kelun, a doctoral student from the College of Environmental Science and Engineering, and Beijing Forestry University is the signature unit of the first author.
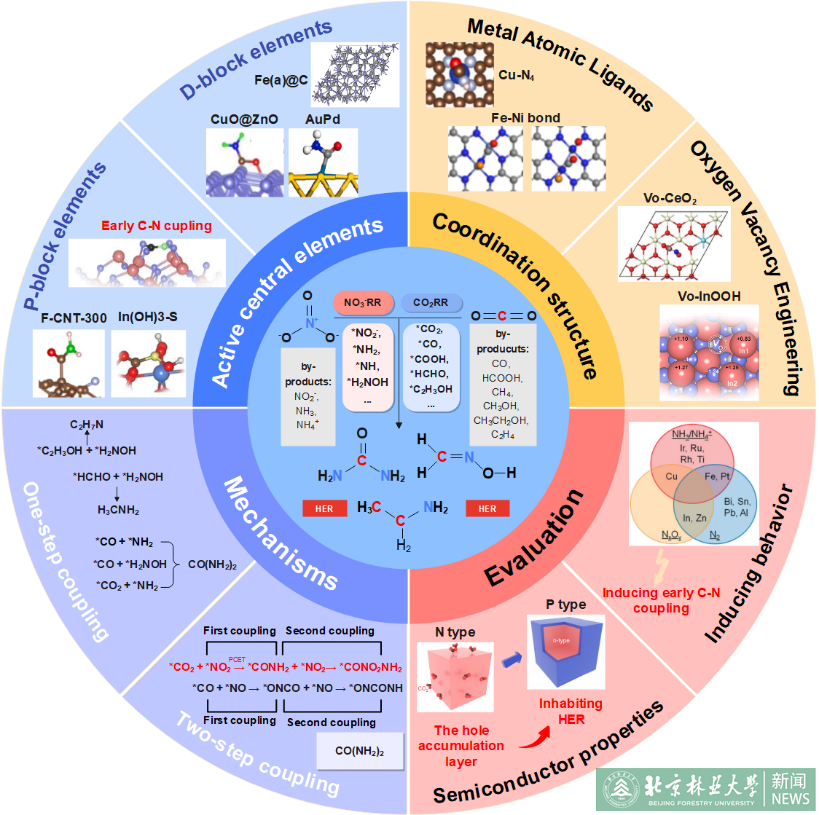
Excess CO2 and NO3- released by human industrial activities have contributed to the deterioration of the global environment. Simultaneous activation and reduction of CO2 and NO3- to produce high-value chemical products is not only effective in solving environmental problems but can also recycle waste pollutants and is essential for the strategic realization of carbon neutrality. Compared with conventional artificial nitrogen and carbon fixation processes, electrochemical C-N coupling of CO2 and NO3- under ambient conditions is an emerging approach. However, the understanding of C-N coupling is still in its infancy, as CO2 and NO3- are first reduced individually to produce different C and N intermediates, which are further coupled to form different types of organic nitrogen compounds through a series of PCET processes. However, this process is often accompanied by the generation of many byproducts. To improve the selectivity of the target products, the design and modulation of catalyst active sites are important. In this paper, a detailed review of the different mechanisms of electrocatalytic coreduction of CO2 and NO3- is presented. From the perspective of controlling competitive reactions, the elements that can achieve C-N coupling in electrocatalysis are divided into p-block elements and d-block elements. The regulatory methods are summarized, and the development potential of each block element is described in terms of the mechanism. Finally, suggestions and challenges for future electrocatalytic coreduction of CO2 and NO3- research are presented.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52270057 and 52070015), Beijing Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 8222061), and Beijing Forestry University Outstanding Young Talent Cultivation Project (No. 2019JQ03007).
Paper link: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2023.123292












