Latest news
The research team led by Associate Professor Han Qiaoling from the College of Technology has made notable advances in identifying functional soil pore structures. Their study, entitled "ACFTransUNet: A new multi-category soil pores 3D segmentation model combining Transformer and CNN with concentrated-fusion attention", has been published in Computers and Electronics in Agriculture with a five-year average impact factor of 6.432.
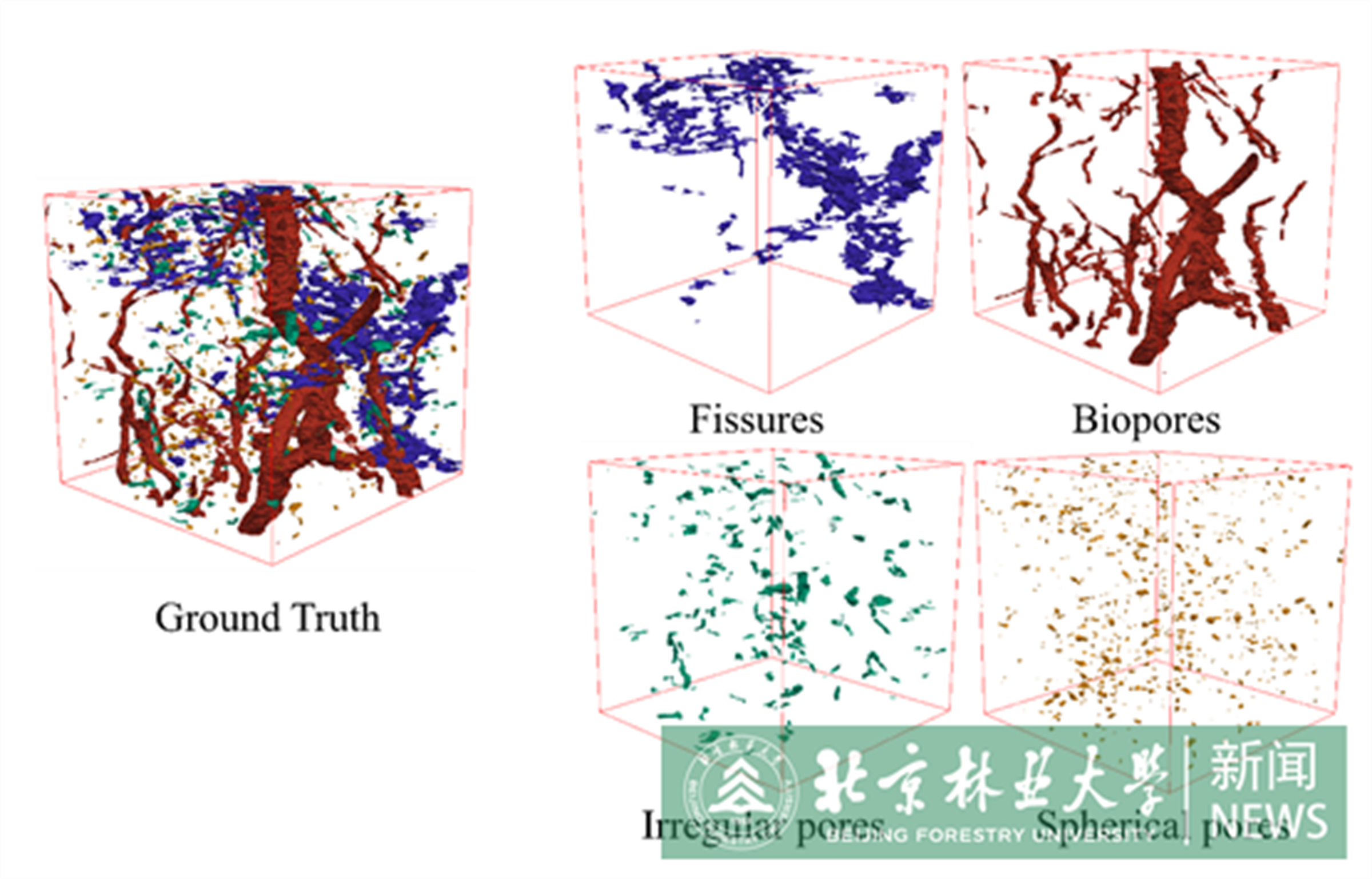

Soil pore structure is an important component of soil systems that has a significant impact on the exchange and storage of soil water, gas, and nutrients. However, current methods for soil different categories pores segmentation have the problem of only having a single category segmentation and low robustness. To address these issues, a dense-connection multi-category three-dimensional (3D) segmentation model named ACFTransUNet using UNet as the backbone network for pore segmentation was proposed to assist in digital soil characterization. Specifically, the concentrated fusion attention (CFA) module is proposed to fuse adjacent encoding layer information, preserve detail feature information of small-volume irregular pores and spherical pores. The encoder's top layer is combined with Head-Transformer module to better extract features of large-volume fissures and biopores. Attention gates are embedded to reduce redundant information and enhance the expression of effective features. Results demonstrate that the ACFTransUNet proposed in this study has the best segmentation performance on self-build soil pore dataset (including fissures, biopores, irregular pores and spherical pores), with MDice, MPrecision, and MAccurary of 85.48 %, 85.30 %, and 94.12 %, respectively. Especially, for irregular pores, compared to the state-of-the-art model, which are improved by 4.25 %, 5.31 %, and 1.04 % in dice, precision, and accuracy, respectively. This study proposes a multi-category segmentation method for soil pores for the first time, providing a scientific basis for revealing soil function and ecosystem service provision by soils within a wider, global context.
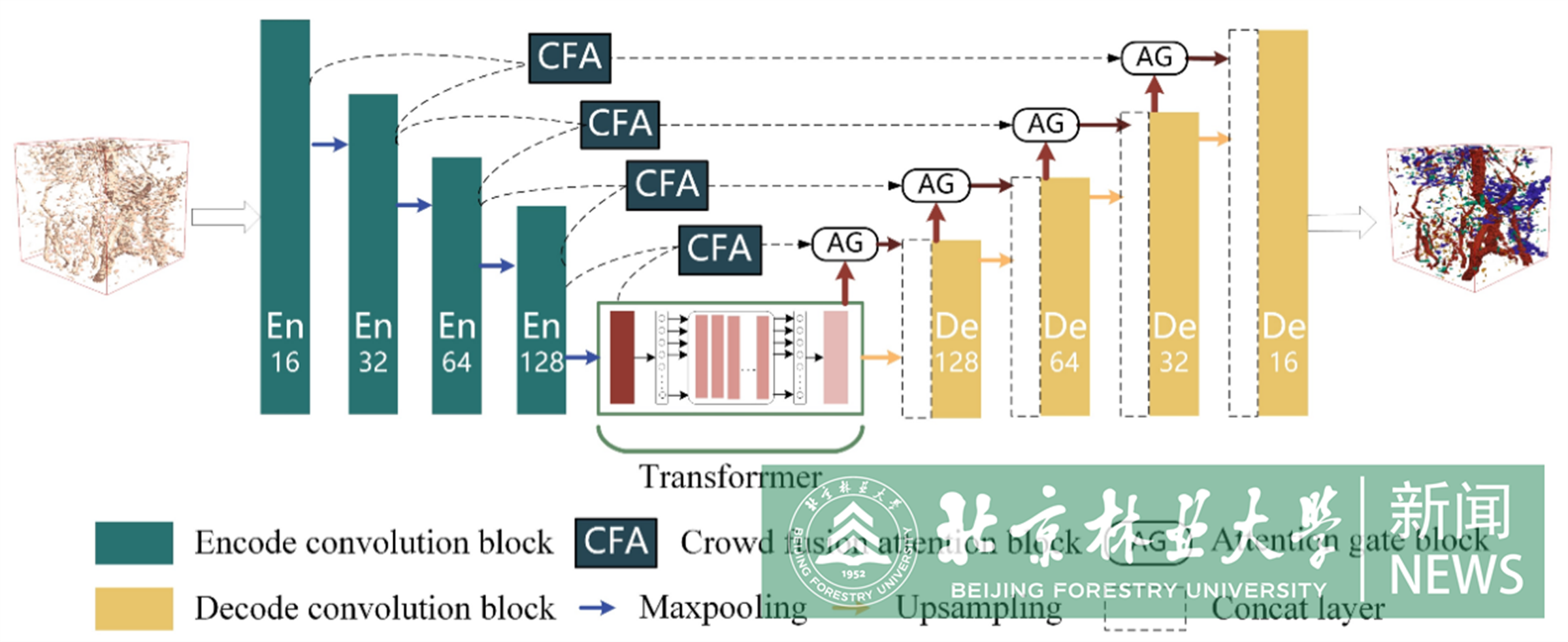
The paper's first author is Song Meihui, a doctoral student at the College of Techonology, with Associate Professor Han Qiaoling serving as the corresponding author. Beijing Forestry University is the signature unit of the paper.
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Youth Foundation of China (32101590), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32071838), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2022T150055), and the Special Fund for Beijing Common Construction Project.
Paper link: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2024.109312
Written by Song Meihui, Han Qiaoling
Translated and edited by Song He
Reviewed by Yu Yangyang












