Latest news
Recently, Professor Shen Yinbai from the College of Biological Sciences and Biotechnology published a paper entitled "The WRKY46-MYC2 module is critical for E-2-hexenal induced anti-herbivore responses by promoting the accumulation of flavonoids" in Plant Communications.

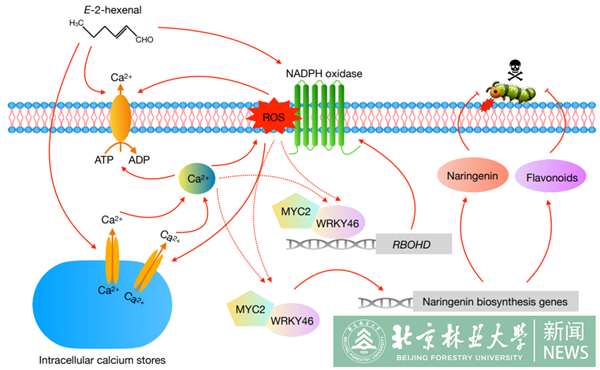
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) play key roles in plant–plant communication, especially under attack by pests. E-2-hexenal is an important component of VOCs, and whether it can induce endogenous insect resistance in plants is not clear. Here, it shows that E-2-hexenal activates early signaling events in Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) mesophyll cells, including an H2O2 burst at the plasma membrane, the directed flow of calcium ions, and an increase in cytosolic calcium concentration. Treatment of wild-type Arabidopsis plants with E-2-hexenal increases their resistance when challenged with the diamondback moth Plutella xylostella L., while the phenomenon is largely lost in wrky46 mutant. Mechanically, E-2-hexenal could induce the expression of WRKY46 and MYC2, their physical interaction was verified using yeast two-hybrid, firefly luciferase complementation imaging, and in vitro pull-down assays. In turn, the WRKY46-MYC2 complex directly binds the promoter of RBOHD to promote its expression through LUC reporter assays, yeast one-hybrid, chromatin immunoprecipitation and electrophoretic mobility shift assays, which also positively regulates the expression of E-2-hexenal-induced naringenin biosynthesis genes (TT4 and CHIL) and the accumulation of total flavonoids, eventually modulates plant tolerance to insects. Together, the research results highlight an important role for WRKY46-MYC2 module in the E-2-hexenal-induced defense response in Arabidopsis, providing new insights into how VOCs trigger defense responses in plants.
Dr. Hao Xin and Dr. Wang Shuyao from Beijing Forestry University and Dr. Fu Yu from China Agricultural University are co-first authors of the paper, and Professor Shen Yingbai is corresponding author. Dr. Yahui Liu and Prof. Libo Jiang from Beijing Forestry University, Dr. Hongyu Shen from the University of Illinois, and Prof. Eric S. McLamore from Clemson University contributed to the study.
Prof. Xie Daoxin from Tschinghua Univerisity provided the myc2 mutant and the LCI vectors, and Prof. Fu Ying from China Agricultural University provided the Y1H vectors and technical support. This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31270655). Paper link: https://www.cell.com/plant-communications/fulltext/S2590-3462(23)00280-8










